Whoops
Whoops is an error handler framework for PHP. Out-of-the-box, it provides a pretty error interface that helps you debug your web projects, but at heart it’s a simple yet powerful stacked error handling system.
Usage
1) Add the dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jooby</groupId>
<artifactId>jooby-whoops</artifactId>
<version>4.0.16</version>
</dependency>2) Install Whoops
import io.jooby.whoops.WhoopsModule;
{
install(new WhoopsModule()); // 1
get("/{id}", ctx -> {
return ctx.path("id").intValue(); // 2
});
}-
Install Whoops
-
Write some exceptional code (see next section)
Test
To test whoops we need to generate an exception. Our route is expecting to get an integer for
the id variable.
-
Open a browser and type
http://localhost:8080/NaN
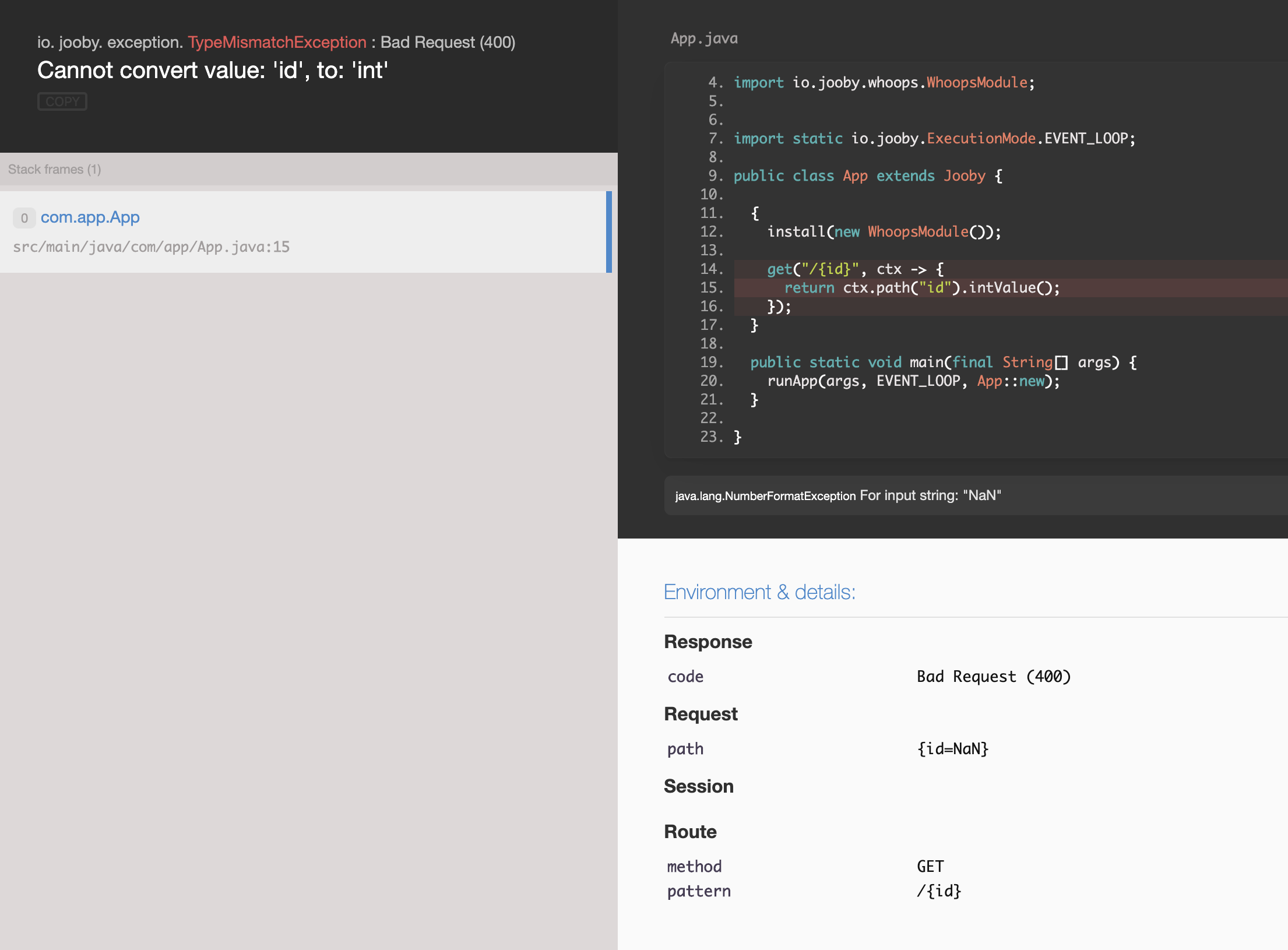
How it works
Whoops only display application frames. That is:
A stacktrace element where we are able to find the source code. The whole stacktrace is available in the application log/console.
Whoops does nothing if there is no source code. An example of this is a 404 request:
Not Found message: Page not found status code: 404
The 404 error is generated by Jooby, not by application code. So whoops let the next exception
handler (which is the default here) to deal with the exception.
If there is no source code to shows, whoops does nothing.
If you have custom error handler just add them before whoops (or after). Remember whoops works like any other Error Handler.
Production deploy
Because whoops only works with source code, whoops won’t ever run in production deployment (unless you deploy with source code).
Still whoops is enabled and will try to find source code in the current application directory.
A better option is to set whoops.enabled = false in your application properties file. This will
completely turn off whoops.